Tiger is a security tool that can be used both as a security audit and as an IDS. It supports multiple UNIX platforms and it is free and provided under a GPL license.
Check all the details on the official website.
Installing Tiger in Ubuntu
Install the application by running the command:
sudo apt-get install tiger
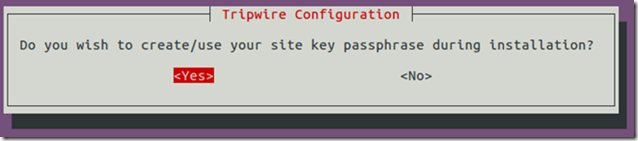
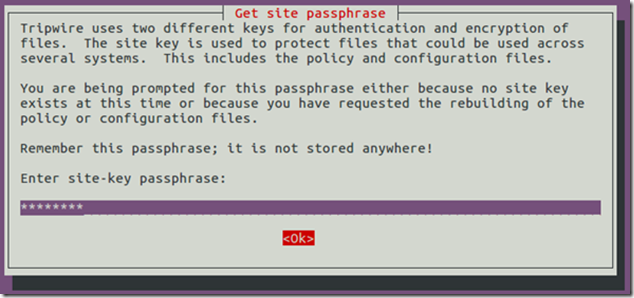
Keys creation:
Done!
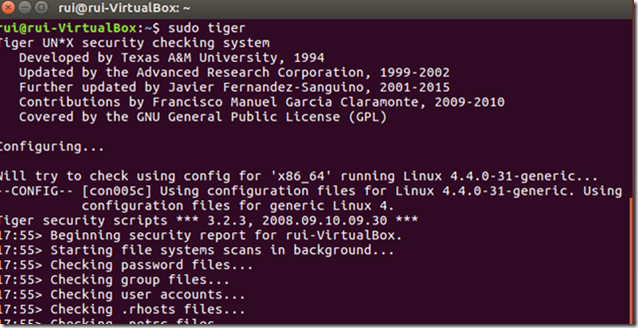
Running Tiger
To start Tiger, just type:
sudo tiger
To check the scan in real time, open another terminal window and go to Tiger’s log folder:
cd /var/log/tiger
If you can´t get there, change your user to root. If you don’t have a root user, create one!
sudo passwd root
NOTE: You can use the “sudo su” command instead. This will prevent using the root user as this is not a good idea when we think about hardening a system
Then use the tail command to see what the Tiger scanner is writing to the log file:
tail -f security.report.rui-VirtualBox.tmp.24839
NOTE: Your log file will have a different name.
To view the final report
less security.report.rui-VirtualBox.170222-18:16
Analyze the log file, identify the vulnerabilities and try to correct them.
Despite being an old tool, Tiger’s simplicity make it the perfect starting point for those who want to start learning about Linux hardening.
Previous post: Windows 7 Hardening (Part II)
Next post: Linux Hardening with Lynis










1 comment:
Good Bolg, thanks for sharing this information.
Oracle Fusion SCM Online Training
Post a Comment