The Open Vulnerability Assessment System (OpenVAS) is a framework of several services and tools offering a comprehensive and powerful vulnerability scanning and management solution.
The security scanner is accompanied with a regularly updated feed of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs), over 51,000 in total (as of February 2017).
OpenVAS Features
The OpenVAS security suite consists of three parts:
- OpenVAS Scanner
- The actual scanner that executes the real-time vulnerability tests;
- It can handle more than one target host at a time;
- Uses the OpenVAS Transfer Protocol (OTP);
- OTP supports SSL.
- OpenVAS Manager
- Handles the SQL Database where all scanning results and configurations are stored;
- Controls the scanner via OTP and offers XML based OpenVAS Management Protocol (OMP);
- It can stop, pause or resume scanning operations;
- Makes user management possible including group level management and access control management.
- OpenVAS CLI
- Command line tool acting as a client for OMP.
Using OpenVAS 8 in Ubuntu 16.04
Installing OpenVAS
Install SQLite for OpenVAS manager.
sudo apt-get install sqlite3
Install other required packages
sudo apt-get -y install python-software-properties
Add Personal Package Archives repository for OpenVAS
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mrazavi/openvas
Update your system
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
Install the OpenVAS package
sudo apt-get install openvas
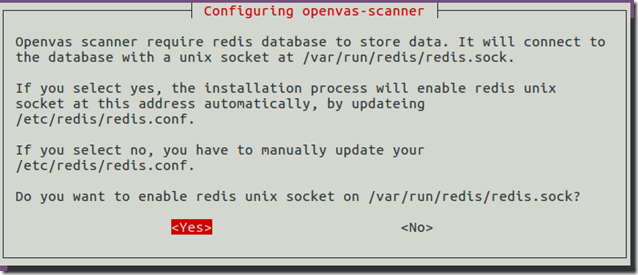
Press Yes
Upgrade vulnerability and compliance data (this will take some time):
sudo openvas-nvt-sync
sudo openvas-scapdata-sync
sudo openvas-certdata-sync
Restart services
sudo /etc/init.d/openvas-scanner restart
sudo /etc/init.d/openvas-manager restart
sudo /etc/init.d/openvas-gsa restart
Create database
sudo openvasmd --rebuild
The installation is complete!
Check installation
The OpenVAS developers provide a handy tool check the state of your application’s installation. To use the tool simply follow these three steps:
1. Download the tool’s latest version:
sudo wget https://svn.wald.intevation.org/svn/openvas/trunk/tools/openvas-check-setup --no-check-certificate
2. Ensure that the script is executable:
sudo chmod +x openvas-check-setup
3. Execute the script:
sudo ./openvas-check-setup
The result might look similar to this:
Fix the errors
sudo openvasmd --rebuild
Running OpenVAS
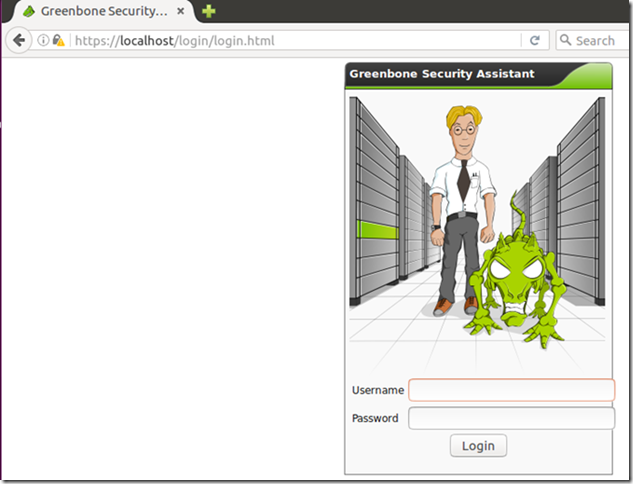
Open your browser (Firefox) and type:
https://localhost/login/login.html
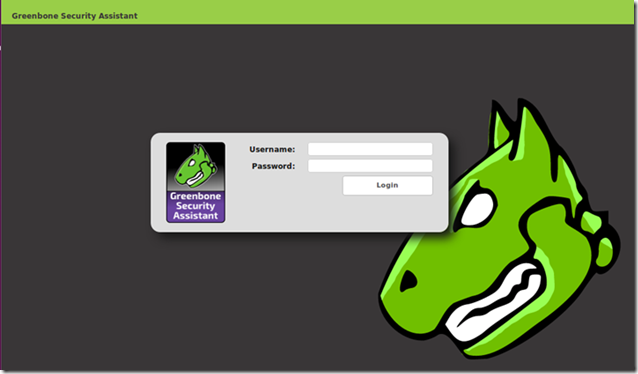
Confirm security exception, and login with user “admin” and password “admin”:
After the successful login, you’ll get to Greenbone’s Security Assistant (GSA) portal:
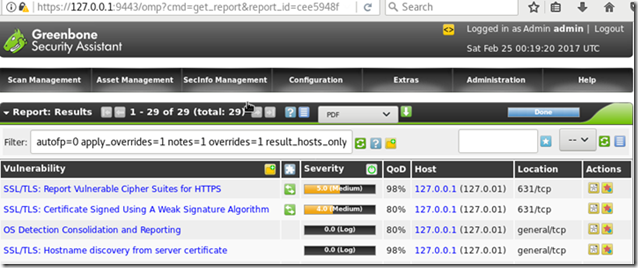
Known vulnerabilities (February 2017)
For a scan of the local machine, just insert the loopback address and press Start Scan
OpenVAS results in Ubuntu
Ultimate scan results:
The final report will display a list of found vulnerabilities and the possible solutions to mitigate or override them.
OpenVAS 9 Beta
A set of new packages for OpenVAS 9 beta is also available. If you want to try it, after installing SQLite and the other packages, just install "openvas9" package instead of "openvas".
Installing in Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install openvas9
Then, update vulnerabilities and compliance data with the following commands:
sudo greenbone-nvt-sync
sudo greenbone-scapdata-sync
sudo greenbone-certdata-sync
Restart services and set database:
sudo service openvas-scanner restart
sudo service openvas-manager restart
sudo openvasmd --rebuild
Please note that the default port number of the GSA has changed to 4000. So, to access the web interface for version 9, go to https://localhost:4000
You can change GSA port number by modifying /etc/default/openvas-gsa file. Then, restart its service by issuing the command:
sudo service openvas-gsa restart
New interface and added features:
Remote scan with OpenVAS 9
Results of a full remote scan on a CentOS 7:
Results of remote full scan on a Fedora 25:
The remote system was identified simply as Linux Kernel
Network scan with OpenVAS 9
The scanner correctly identified Windows Server 2012/10 machines and Ubuntu/CentOS:
This means OpenVAS can also be used to harden Windows machines
Using OpenVAS 8 in Fedora 25
In Fedora, OpenVAS can be installed either from the official repository or from the Atomic repository.
Installing OpenVAs
Install from the official repository
sudo su
Disable SELinux
vi /etc/selinux/config
Change the line SELINUX=disabled
Reboot your system
Install the application
sudo su
dnf install openvas-gsa openvas-manager openvas-scanner openvas-cli
Install additional packages
dnf install texlive-latex nmap alien mingw32-nsis
Start service
systemctl start openvas-manager
Create certificate
openvas-mkcert
Install REDIS service
dnf install redis -y
Configure the REDIS service
vi /etc/redis.conf
Uncomment lines:
- unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock
- unixsocketperm 700
Update vulnerabilities and compliance data
openvas-nvt-sync
openvas-scapdata-sync
openvas-certdata-sync
Create client certificate
openvas-mkcert-client -n -i
Set database
systemctl start openvas-scanner
openvasmd --rebuild
Create OpenVAS Manager Admin user
openvasmd --create-user=admin --role=Admin && openvasmd --user=admin --new-password=admin
Start services
systemctl start redis
systemctl start openvas-manager
systemctl start openvas-scanner
systemctl start openvas-gsa
Check installation
openvas-check-setup
Running OpenVAS
Open Firefox and go to:
Start a local scan:
OpenVAS results in Fedora:
Network scan:
Like in Ubuntu, you’ll get a list of specific items that were found and the threats will be color-coded. For instance, this is one of the high threats:
As you can see, the report also includes information about how to address the issue.
Besides, the application will recognize and scan Windows machines!
Conclusion
OpenVAS is a magnificent tool to spot vulnerabilities and highlight areas to focus on when you are hardening your system.
This was just a quick introduction, showing a bare minimum of the functionality of the OpenVAS security suite. Explore the Greenbone Security Assistant interface and take advantage of the great built-in help system to learn more about your options.
For instance, using the application with the proper credentials to logon to remote machines will allow it to make better scanning.
Besides, among other tasks, you can easily schedule scans, automatically generate reports, and email alerts when certain threat levels are generated.
Previous post: Linux Hardening with Lynis
Next post: Linux Hardening with OpenSCAP
























2 comments:
Good information. Oracle Fusion SCM Online Training
This is an excellent post I seen thanks to share it. It is really what I wanted to see hope in future you will continue for sharing such a excellent post. ivrs
Post a Comment